Diving deep into the world of retirement planning for the self-employed, this introduction sets the stage for an exciting journey filled with financial wisdom and strategic insights. Get ready to explore the ins and outs of securing your future like a boss!
In the following paragraphs, we’ll break down the essentials of retirement planning, from account options to investment strategies, tailored specifically for the self-employed hustlers out there.
Importance of Retirement Planning for Self-Employed
Retirement planning is crucial for self-employed individuals to ensure financial security and stability during their retirement years. Unlike traditional employees who may have access to employer-sponsored retirement plans, self-employed individuals are responsible for creating their own retirement savings strategy.
Differences in Retirement Planning
Self-employed individuals have the flexibility to choose from a variety of retirement savings options, such as SEP-IRAs, Solo 401(k)s, or SIMPLE IRAs. They can tailor their retirement plan to suit their financial goals and investment preferences. In contrast, traditional employees often have limited choices and are subject to the retirement plan offered by their employer.
Risks of Not Having a Retirement Plan
Not having a retirement plan in place can expose self-employed individuals to financial uncertainty and instability in their later years. Without sufficient savings, they may have to rely solely on Social Security benefits, which may not be enough to maintain their desired standard of living. Additionally, procrastinating retirement planning can lead to missed opportunities for compound interest growth and tax benefits that come with starting a retirement plan early.
Retirement Account Options for Self-Employed
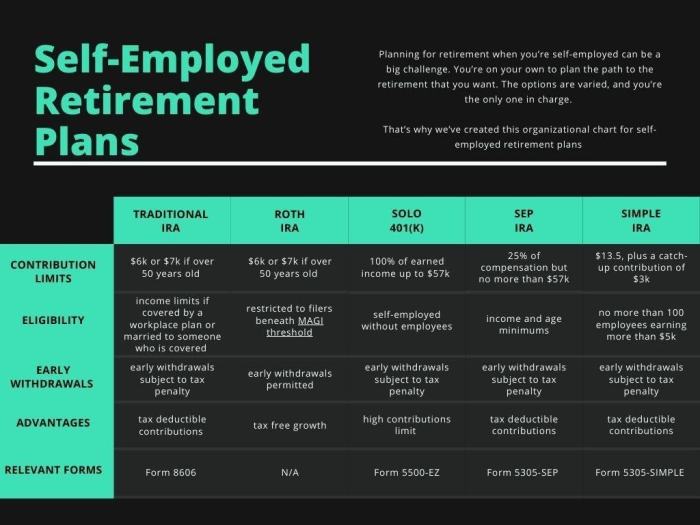
When it comes to planning for retirement as a self-employed individual, there are several retirement account options to consider. Each type of account has its own features, benefits, contribution limits, eligibility criteria, and tax implications. It’s important to understand these differences to make the best choice for your financial future.
Solo 401(k)
The Solo 401(k) is a retirement account designed for self-employed individuals or business owners with no employees other than a spouse. Here are some key points to consider:
- Contribution Limits: As of 2021, you can contribute up to $58,000 ($64,500 if you are 50 or older) or 100% of your income, whichever is less.
- Eligibility Criteria: Must be self-employed or a business owner with no full-time employees other than a spouse.
- Tax Implications: Contributions are tax-deductible, and earnings grow tax-deferred until withdrawal.
SEP IRA (Simplified Employee Pension Individual Retirement Account)
A SEP IRA is another option for self-employed individuals, offering simplicity and flexibility. Here’s what you need to know:
- Contribution Limits: As of 2021, you can contribute up to 25% of your net earnings from self-employment, up to $58,000.
- Eligibility Criteria: Available to self-employed individuals and small business owners with one or more employees.
- Tax Implications: Contributions are tax-deductible, and earnings grow tax-deferred until withdrawal.
SIMPLE IRA (Savings Incentive Match Plan for Employees Individual Retirement Account)
The SIMPLE IRA is a retirement plan that allows small businesses with 100 or fewer employees to offer a retirement savings plan. Here are some important details:
- Contribution Limits: As of 2021, you can contribute up to $13,500 ($16,500 if you are 50 or older) with a required employer match contribution.
- Eligibility Criteria: Available to self-employed individuals and small businesses with 100 or fewer employees.
- Tax Implications: Contributions are tax-deductible, and earnings grow tax-deferred until withdrawal.
Strategies for Retirement Savings
Saving for retirement is crucial, especially for self-employed individuals who don’t have access to employer-sponsored retirement plans. Here are some strategies to help maximize retirement savings and secure your financial future.
Importance of Diversification
Diversification is key when it comes to retirement investment portfolios. By spreading your investments across different asset classes, you can reduce risk and potentially increase returns. Consider investing in a mix of stocks, bonds, real estate, and other assets to create a well-rounded portfolio.
Catch-Up Contributions
As you near retirement age, you may be eligible to make catch-up contributions to your retirement accounts. This allows you to contribute additional funds beyond the normal limits set by the IRS. Take advantage of catch-up contributions in your 401(k), IRA, or other retirement accounts to boost your savings and make up for lost time.
Managing Investments for Retirement
Investing for retirement as a self-employed individual is crucial for building a secure financial future. It involves making informed decisions based on your risk tolerance, investment goals, and monitoring your portfolio over time to ensure it aligns with your retirement objectives.
Risk Tolerance and Investment Goals
Understanding your risk tolerance is essential when managing investments for retirement. This refers to your comfort level with the possibility of losing money in exchange for potentially higher returns. Your investment goals, such as the age you plan to retire or the lifestyle you envision, will also influence your investment strategy.
- Assess your risk tolerance: Consider factors like your age, financial situation, and long-term goals to determine how much risk you are willing to take.
- Set clear investment goals: Define your retirement objectives, including the desired income level, retirement age, and any specific financial milestones you want to achieve.
- Diversify your portfolio: Spread your investments across different asset classes to reduce risk and maximize returns over the long term.
Monitoring and Adjusting Investment Portfolios
Regularly monitoring and adjusting your investment portfolio is vital to ensure it remains in line with your retirement goals and risk tolerance. Rebalancing your portfolio, reviewing your investments, and staying informed about market trends can help you make informed decisions and optimize your retirement savings.
- Review your investments periodically: Assess the performance of your investments and make adjustments based on changes in your financial situation or market conditions.
- Rebalance your portfolio: Maintain the desired asset allocation by periodically rebalancing your portfolio to manage risk and stay on track with your investment goals.
- Stay informed: Keep up with financial news, market trends, and investment opportunities to make well-informed decisions and adapt your investment strategy as needed.
