Diving into the world of calculating debt-to-income ratio, this intro will take you on a ride through the ins and outs of managing your finances like a boss. Get ready to learn the ropes and take control of your financial future in style.
Get ready to uncover the secrets of financial planning and how debt-to-income ratio plays a crucial role in keeping your money game strong.
Understanding Debt-to-Income Ratio
Debt-to-Income (DTI) Ratio is a financial metric used to measure an individual’s or household’s monthly debt payments relative to their gross monthly income. It is a crucial factor in determining one’s financial health and stability.
Importance of Debt-to-Income Ratio
Maintaining a healthy DTI ratio is vital for financial planning as it helps lenders assess an individual’s ability to manage monthly payments and take on additional debt responsibly. A low DTI ratio indicates that a person has a manageable level of debt compared to their income, making them a more attractive borrower.
- Having a low DTI ratio can increase the likelihood of loan approval and favorable interest rates.
- It also serves as a good indicator of overall financial well-being and helps individuals make informed decisions about taking on new debt.
- Monitoring your DTI ratio regularly can help prevent financial strain and potential default on debt obligations.
Calculating Debt-to-Income Ratio
To calculate your DTI ratio, you need to add up all your monthly debt payments and divide it by your gross monthly income. The formula is as follows:
DTI Ratio = (Total Monthly Debt Payments / Gross Monthly Income) x 100
- Monthly debt payments include mortgage or rent, car loans, credit card minimum payments, student loans, and any other outstanding debts.
- Gross monthly income refers to your total income before taxes and deductions.
Components of Debt-to-Income Ratio
When calculating your debt-to-income ratio, it’s important to understand the different components that make up this crucial financial metric. Your debt-to-income ratio is a key factor that lenders consider when determining your creditworthiness and ability to manage additional debt responsibly.
Total Monthly Debt Payments
- Your total monthly debt payments include all recurring financial obligations that you have, such as mortgage or rent, car loans, student loans, credit card payments, and any other debts you may have.
- Having a high total monthly debt payment can indicate that you may be overextended financially and have less disposable income to cover new loan payments, affecting your ability to take on new debt.
- For example, if your total monthly debt payments amount to $2,000 and your gross monthly income is $6,000, your debt-to-income ratio would be 33% ($2,000/$6,000).
Gross Monthly Income
- Your gross monthly income is the total amount of money you earn before taxes and deductions are taken out. This includes your salary, wages, tips, bonuses, alimony, and any other sources of income.
- A higher gross monthly income generally indicates a greater ability to manage debt, as you have more income available to cover your monthly expenses and debt payments.
- For instance, if your gross monthly income is $6,000 and your total monthly debt payments amount to $2,000, your debt-to-income ratio would be 33% ($2,000/$6,000).
Calculating Debt-to-Income Ratio
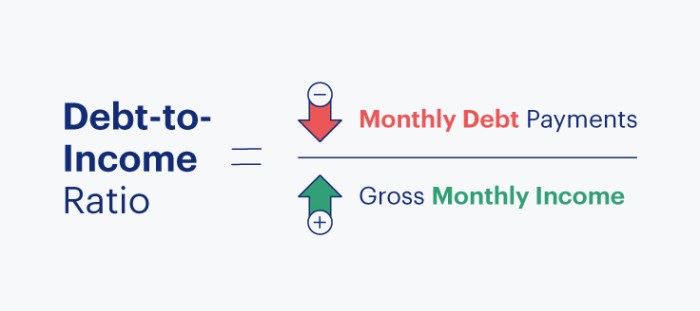
To calculate your debt-to-income ratio, you need to add up all your monthly debt payments and divide it by your gross monthly income. This ratio is expressed as a percentage.
Ideal Debt-to-Income Ratio Range
An ideal debt-to-income ratio range for financial stability is typically 36% or lower. This means that your total monthly debt payments should not exceed 36% of your gross monthly income.
Tips to Improve High Debt-to-Income Ratio
- Increase your income: Consider taking up a side hustle or asking for a raise at work to boost your income.
- Reduce your debt: Create a plan to pay off high-interest debts first and work towards reducing your overall debt load.
- Cut down on expenses: Look for areas where you can reduce spending, such as eating out less or canceling subscription services.
- Consolidate debts: Consider consolidating high-interest debts into a lower interest loan to make payments more manageable.
Importance of Debt-to-Income Ratio
Understanding the importance of debt-to-income ratio is crucial for managing your financial health and making informed decisions.
Lender’s Perspective
- Lenders use the debt-to-income ratio as a key factor in determining a borrower’s creditworthiness and ability to repay a loan.
- A lower debt-to-income ratio indicates that a borrower has more disposable income available to meet their monthly loan payments.
- Having a lower ratio can increase the chances of loan approval and potentially secure better terms and interest rates.
Impact on Credit Score
- Your debt-to-income ratio plays a significant role in determining your credit score.
- A high ratio can negatively impact your credit score, making it harder to qualify for new credit or loans.
- By keeping your debt-to-income ratio low, you can improve your credit score over time and enhance your overall financial health.
Real-Life Examples
- For example, if you have a high debt-to-income ratio due to multiple outstanding loans and credit card balances, it may signal to lenders that you are overextended and pose a higher risk.
- On the other hand, maintaining a healthy debt-to-income ratio by keeping your debts in check can lead to more favorable financial opportunities, such as lower interest rates on loans and better credit card offers.
